Lumbar Laminectomy
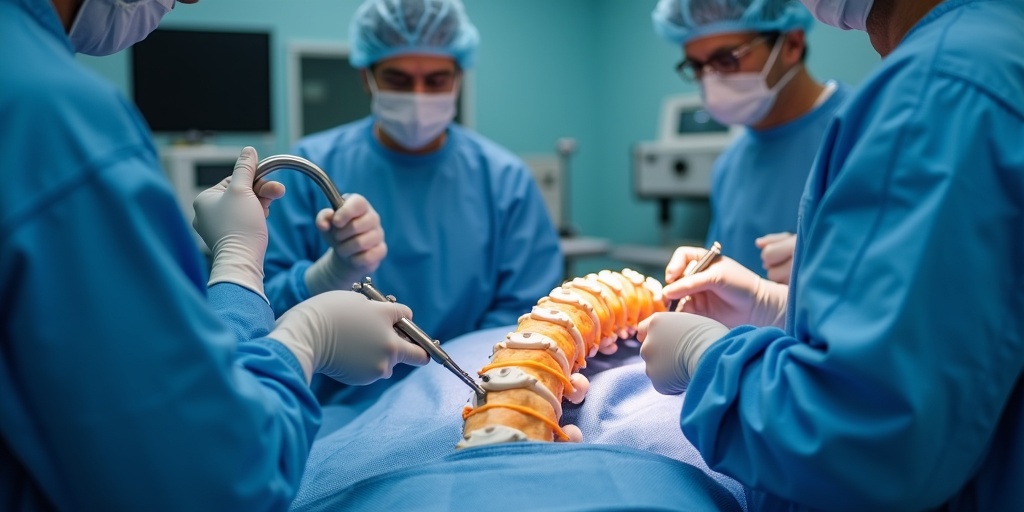
Lumbar laminectomy removes bone and ligament that compress spinal nerves, restoring your ability to walk comfortably. This proven procedure relieves the leg pain, numbness, and weakness caused by spinal stenosis.
When Laminectomy Is Recommended
- Neurogenic claudication (leg pain when walking)
- Spinal stenosis with nerve compression
- Difficulty walking more than 1-2 blocks
- Leg weakness or numbness when standing
- Conservative treatment hasn't provided relief
How Laminectomy Works
Precise Access
Small incision over the affected spinal level
Bone Removal
Remove lamina and thickened ligaments
Nerve Decompression
Create space for nerves to function normally
Minimally Invasive Options
Dr. Greenberg uses advanced techniques including tubular retractors and endoscopic approaches when appropriate, reducing tissue damage and accelerating recovery.
Benefits of Laminectomy
- Dramatically improved walking distance
- Relief from leg pain and numbness
- Restored strength and balance
- Same-day surgery options available
- Preserves spinal stability
- High success rate for symptom relief
Risks & Considerations
- Infection, bleeding, or anesthesia risks
- Nerve injury (rare with experienced surgeons)
- Spinal fluid leak (usually heals spontaneously)
- Incomplete symptom relief in some cases
Recovery Timeline
Surgery Day
Walking within hours; many patients go home same day
Early Recovery
Gradual increase in walking distance; avoid heavy lifting
Functional Return
Return to work and normal activities; physical therapy
Full Recovery
Maximum walking tolerance achieved; return to all activities
Ideal Candidates
- Confirmed spinal stenosis on MRI
- Symptoms match imaging findings
- Failed conservative treatment for 3+ months
- Good overall health for surgery
- Realistic expectations about outcomes
Alternative Treatments
Conservative Options
- • Physical therapy and core strengthening
- • Epidural steroid injections
- • Activity modification and assistive devices
- • Anti-inflammatory medications
Surgical Alternatives
- • Endoscopic decompression
- • Laminotomy (partial removal)
- • Fusion if instability present
- • Interspinous spacers
Why Choose Greenberg Spine
Fellowship Training
Advanced training at Mayo Clinic, Johns Hopkins, and Brown University
Advanced Technology
Minimally invasive and endoscopic techniques for faster recovery
Patient-Centered Care
Outpatient focus with personalized treatment plans
What to Expect
Pre-Operative
- • Comprehensive evaluation and imaging review
- • Medical clearance if needed
- • Pre-operative instructions and preparation
Surgery Day
- • General anesthesia with monitoring
- • 1-3 inch incision depending on approach
- • Same-day discharge for many patients
Frequently Asked Questions
Ready to Walk Pain-Free Again?
Schedule a consultation to discuss if lumbar laminectomy is right for your spinal stenosis.
Related Procedures
Related Topics
Learn more about related conditions and treatments
Ready to take the next step?
Schedule a consultation with Dr. Greenberg to discuss your spinal health and treatment options.
Information is educational, not medical advice. Outcomes vary. Consult Dr. Greenberg for personalized evaluation and treatment recommendations.
MIS Lumbar Laminectomy & Laminotomy
Minimally invasive spine decompression procedures to relieve nerve pressure with faster recovery
MIS Laminotomy
MIS laminotomy is a minimal decompression where only the minimum necessary bone is removed to decompress a specific nerve root, making it even less invasive than full laminectomy.
When It's Used
- Foraminal stenosis (stenosis at nerve exit)
- Single nerve root compression
- Localized stenosis
- Minimal canal involvement
The Procedure
- Very small incision (18mm or less)
- Only small amount of lamina removed
- Lateral recess decompressed
- Minimal bone removal
- Motion fully preserved
- Procedure time: 45-90 minutes
Advantages
- Most motion-preserving approach
- Smallest bone removal
- Fastest recovery
- Minimal tissue trauma
- Often outpatient
Success Rate
- 80-90% pain relief
- 85% satisfaction
- Minimal re-stenosis risk
- Long-term stable
Recovery Timeline
- Surgery day: Often same-day discharge or next morning
- Week 1-2: Light activity
- Week 2-3: Return to work likely
- Week 3-4: Most normal activities
- Week 4-6: Full activity
Hospital Stay
Outpatient or overnight
Risks (Rare)
- Dural tear (<1%)
- Nerve injury (<1%)
- Infection (0.5%)
- Bleeding (<1%)
- Incomplete decompression (5-10%)
Questions About MIS Laminotomy?
Dr. Greenberg specializes in minimally invasive spine procedures with excellent outcomes.